Cloud platforms continue to rise nowadays, and several companies have different models and types of cloud computing.
Do you know the main types of cloud computing?
First, cloud computing consists of a distributed system offered by a third party that you pay to use the services.
What is a distributed system?
A distributed system consists of several devices and servers that operate together harmoniously, however, disjoint in their location.
To the user, a distributed system looks like a single operating system. However, they may be globally distributed and remotely managed data centers.
Companies commonly create private cloud computing that would only be accessed by authorized personnel.
This private state of the cloud exists and comprises the main types of existing clouds.
So, let’s understand the cloud types: Private, Public, and Hybrid.
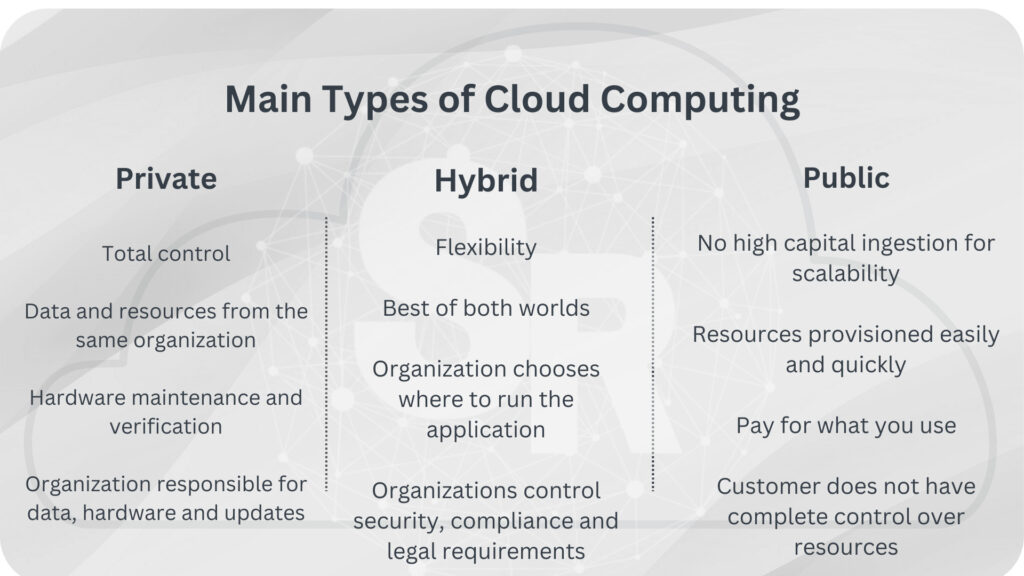
Private Cloud
Let’s start with a private cloud. A private cloud is the natural evolution of an enterprise data center.
It is a cloud (delivering IT services over the internet) used by a single entity.
The private cloud offers greater control for the company and its IT department. However, it also has higher costs and fewer benefits than a public cloud deployment.
Finally, you can host a private cloud in our on-premises data center. It could also be hosted in a dedicated offsite data center, possibly even by a third party that has dedicated that data center to your company.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a computing environment that uses public and private clouds in an interconnected environment.
We can use a hybrid cloud environment to allow a private cloud to emerge to temporarily increase demand by deploying public cloud resources.
Additionally, we can use hybrid cloud computing to provide an extra layer of security.
For example, users can flexibly choose which services to keep in the public cloud and which to deploy in their private cloud infrastructure.
Public Cloud
In this type of cloud computing provider, there is no restriction regarding access. Anyone can create an account and connect to the cloud.
In this model, the client does not have complete control over network resources. Therefore, our responsibilities vary by service model.
To better understand the role of the customer and the provider, read our article – Understand the shared-responsibility model.
In public cloud computing, applications are rapidly provisioned. Hence, there is the notion of “infinite” resources due to quickly allocating resources.
The resource usage model is mainly mode-based, which means paying for what you use.
Many organizations have migrated to cloud computing for ease of resource allocation and associated low costs.
Enterprise cloud adoption is driven by the costs associated with building and maintaining an on-premises data center.
There is a trade-off, wich means that you do not have full control of the cloud features. In some cases, not having full control can be a complicating factor.
However, companies can still own their data center and use public cloud resources.
See other topics on the site:
- Python get metadata from images and pdfs
- How to use Ngrok
- Install ubuntu 24 on virtualbox
- How to X11 Forwarding using SSH
- How to handle PDF in Python?

Juliana Mascarenhas
Data Scientist and Master in Computer Modeling by LNCC.
Computer Engineer

