Are you ready to take the first step into the fascinating world of computer networks? In this step-by-step and super easy tutorial, we will use Packet Tracer, Cisco’s network simulator, to create your first functional network.
We will start from scratch, setting up a basic network with just 2 computers. Don’t worry about complex technical terms – we will simplify everything and show you that creating your first network in Packet Tracer can be easier and more fun than you imagine!
Get ready to set up your first virtual networking lab and kickstart your journey into the world of networking!
Choosing Devices in Packet Tracer
The first step is to choose the two computers we will use in our first network. To do this, go to the lower menu and select “End devices”.
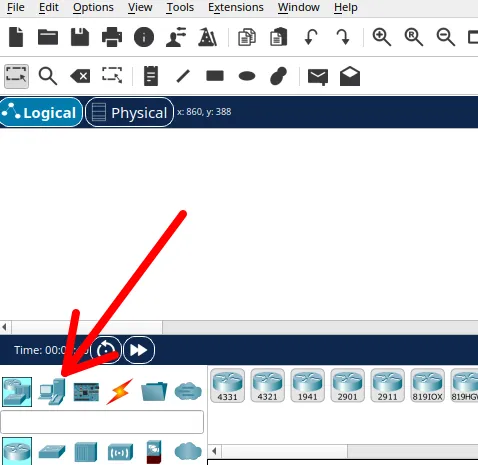
After clicking on “end devices“, select the device named “PC“. The “PC” will be the computer we will use in our network.
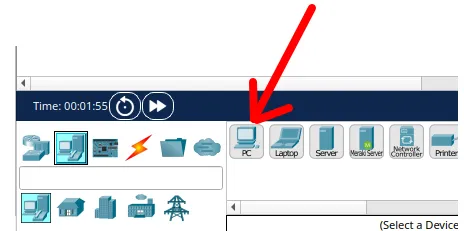
Now, click on the “PC” and drag it onto the workspace where you want to position it. Once you have clicked and dragged with the mouse, release the button at the desired location.
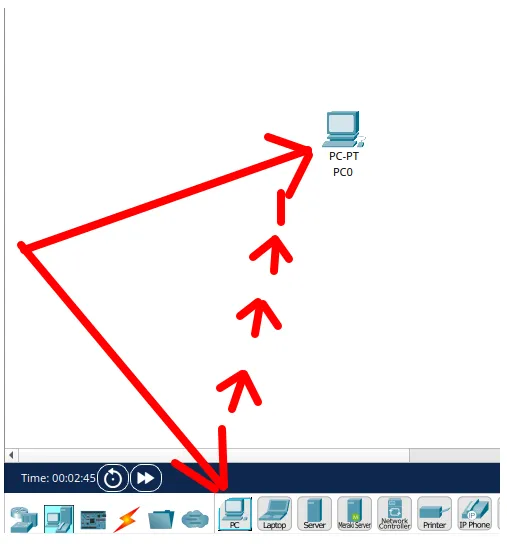
Do the same for the second “PC”. In the end, you will see two “PCs” on the screen: “PC0” as our first “PC” and “PC1” as our second “PC”.

Connecting Devices in Packet Tracer
The image below shows how we will connect the two devices we inserted into our network.
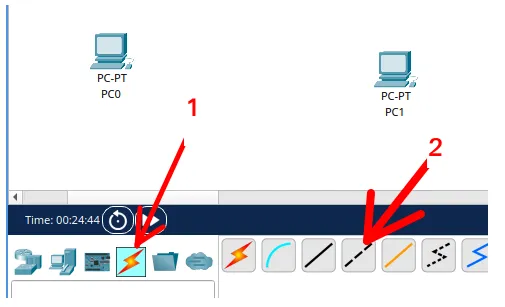
To do this, click on the lightning bolt icon “Connections” represented by arrow 1 and then choose the cable type as “Copper Cross-Over” in arrow 2.
The “Copper Cross-Over“, also known as a twisted pair cable, is used when connecting two devices that also operate at layer 3.
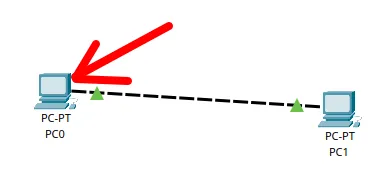
After clicking on “Copper Cross-Over“, click on one “PC” and then click on the other computer as shown in the images below.
When clicking on the computer after selecting “Copper Cross-Over“, select “FastEthernet0” as shown in the images below.

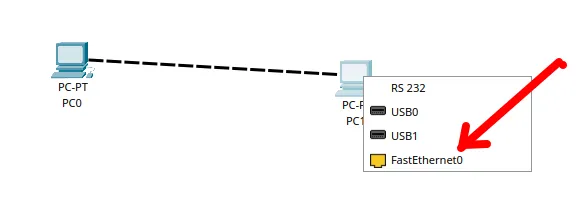
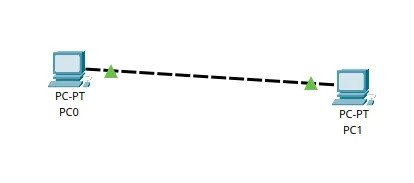
After selecting “FastEthernet0” for both “PCs”, you will see a network setup as shown in the image below.
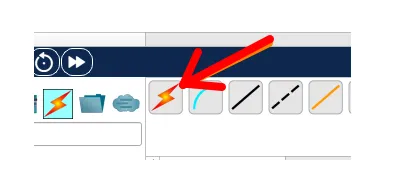
Whenever you have doubts about which cable to use to connect devices in Packet Tracer, you can use the button with the lightning bolt icon labeled “Automatically Choose Connection Type“.
This button, which can be seen in the figure below, will choose the correct cabling for your device.
Assigning IP Addresses to Devices in Packet Tracer
Now, let’s assign IP addresses to our devices so they can communicate. First, double-click on the first “PC”.
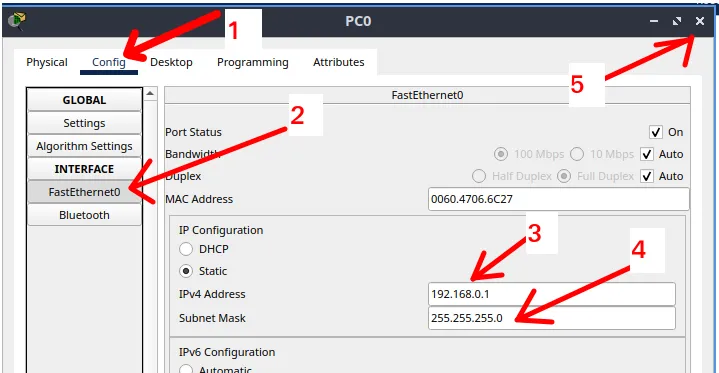
After double-clicking on the first “PC”, we will follow the steps described below and shown in the figure below.
- 1: Click on “Config” in the top menu.
- 2: Select the network interface of the device, in this case, “FastEthernet0“.
- 3: Enter the device’s IP address, in this case, “192.168.0.1“.
- 4: Enter the subnet mask, which in this case is “255.255.255.0“.
- 5: Click the exit button to close the configuration window.
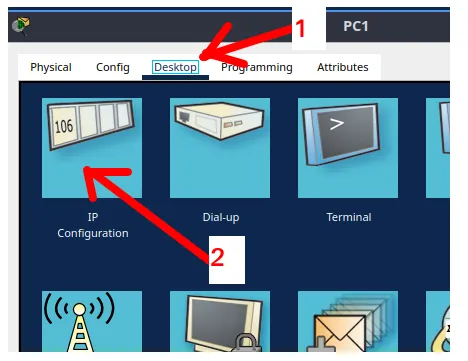
Now, let’s double click on the other computer “PC”.
Next, we will click “Desktop” in the top menu and then click “IP Configuration” as shown by arrow 2. We are doing these steps to show another way to insert IP into end devices.
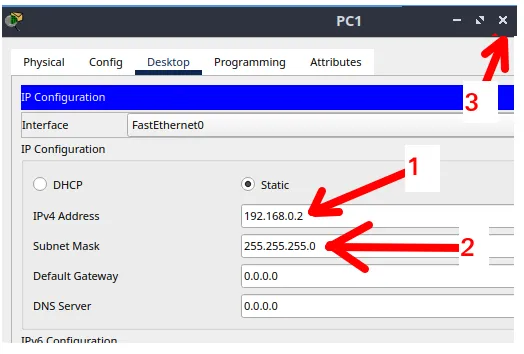
Now, let’s insert the IP configuration for the second device following the steps below and shown in the figure below.
- 1: here we will enter the IP of the device. In this case, the IP is “192.168.0.2“
- 2: here we will insert the net mask. In this case, it will be “255.255.255.0“
- 3: Let’s click the exit button to be able to exit the configuration window.
Testing Device Connectivity in Packet Tracer
Once the IPs are configured, we can test the connectivity between the devices. Below are two different ways to test connectivity between devices.
Testing Connectivity with Ping in Packet Tracer
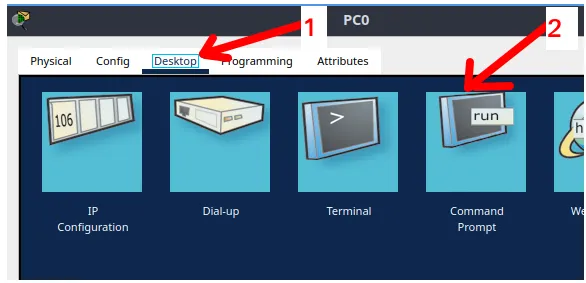
To use ping to test connectivity, double-click on one of the devices, then go to “Desktop” and select “Command Prompt“.
In the command window, type the following command to test connectivity:
ping 192.168.0.2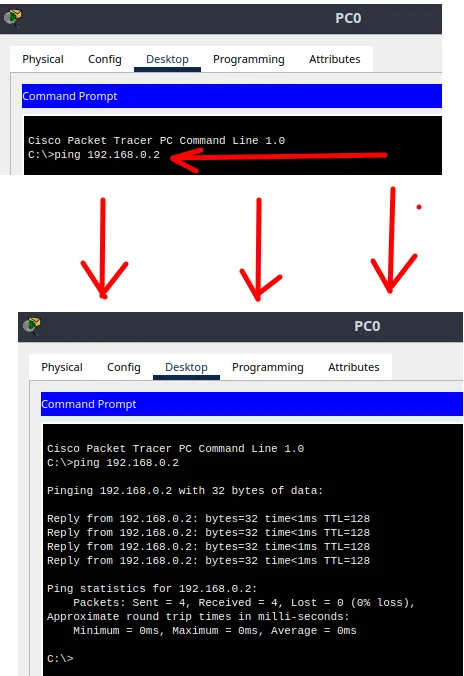
This command “ping 192.168.0.2” is used to send an ICMP packet from the source device “192.168.0.1” to the destination device “192.168.0.2“.
If you receive a response, it indicates that there is connectivity between the devices.
Testing Connectivity with the Letter on Packet Tracer
In the top menu of the Packet Tracer we have a button with a closed card icon. Let’s use this “Simple PDU” button to test cross-device connectivity.
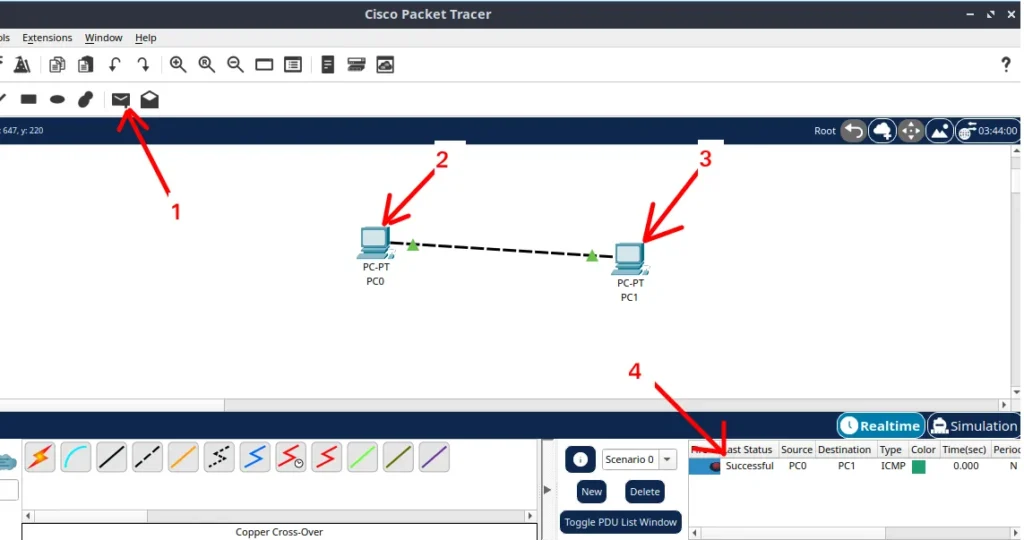
To take the test we will follow the steps below and see the picture below.
- 1: Click the button that has a closed letter “Simple PDU“.
- 2: Click on the device that will be the origin.
- 3: Click on the device that will be the destination.
- 4: We can see the result of the connectivity test. In that case we can see that it was a success.podemos ver que foi um sucesso.
Checking the ARP Table of a Computer in Packet Tracer
If you want to see the ARP table of a “PC”, first perform a ping as described above. Then, in the same command window, type the following command:
arp -a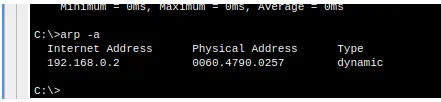
In this case, we will see a screen like the one in the figure above. This figure shows the ARP table of the ping source device.
In this ARP table, we can see the IP of the destination device “192.168.0.2” and the MAC of the destination device.
See more:
- Lesson 1: Install Packet Tracer on Linux
- Lesson 2: Packet Tracer for Dummies: Setting Up Your First Network with 2 PCs (Quick Start Guide)
- Lesson 3: Create Network Switch packet tracer
- Lesson 4: Packet Tracer network with one router
Learn how to use the curl command: tutorial with practical examples
Tutorial: How to use WHOIS and RDAP
How to Set Up a Postfix and Dovecot Email Server on Linux: A Step-by-Step Guide

Juliana Mascarenhas
Data Scientist and Master in Computer Modeling by LNCC.
Computer Engineer

