The WHOIS or RDAP service is an essential tool for obtaining information about domains, IPs, and DNS records. In this tutorial, we will learn how to use WHOIS/RDAP.
Difference Between WHOIS and RDAP
WHOIS is a communication protocol that allows you to obtain information about a domain, IP, or DNS record. The service is maintained by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) and is used to verify the ownership and management of domains and IPs.
ICANN’s Registration Data Lookup Tool allows you to query current registration data for domain names and Internet numeric resources. It uses the RDAP (Registration Data Access Protocol), which replaces the WHOIS protocol.
RDAP offers advantages such as more secure access to data, a standardized and user-friendly format, support for internationalization, and differentiated access to registration data.
More information can be found on ICANN’s Registration Data page.
How to Search on WHOIS or RDAP
To perform a search on WHOIS / RDAP, open a browser and enter the site below.
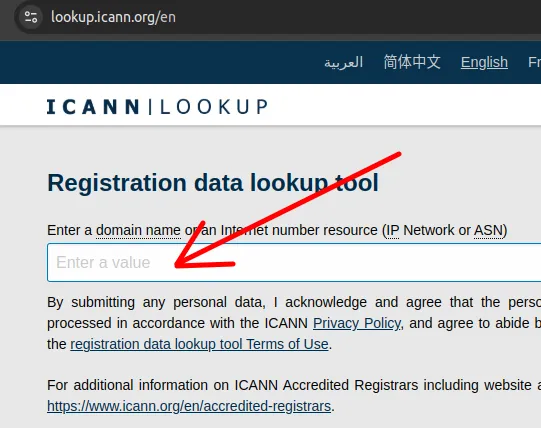
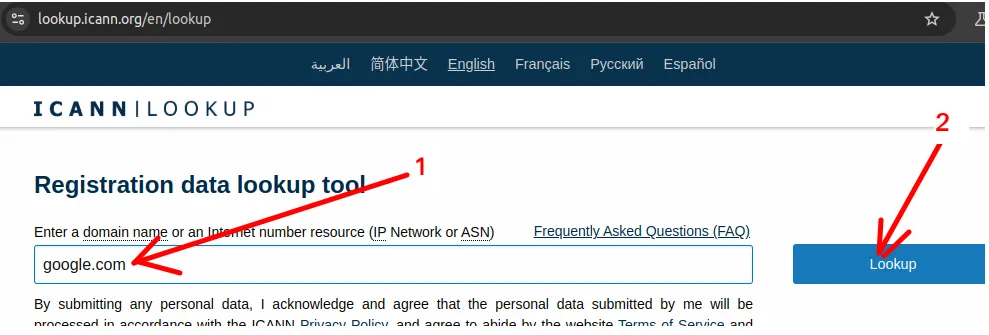
Next, type the site you want to check and click “Lookup“.
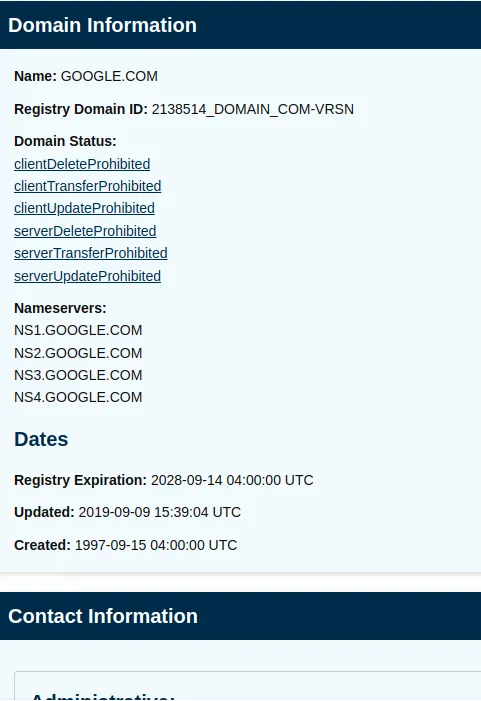
The figure below shows the information RDAP provided about the site we wanted to verify.
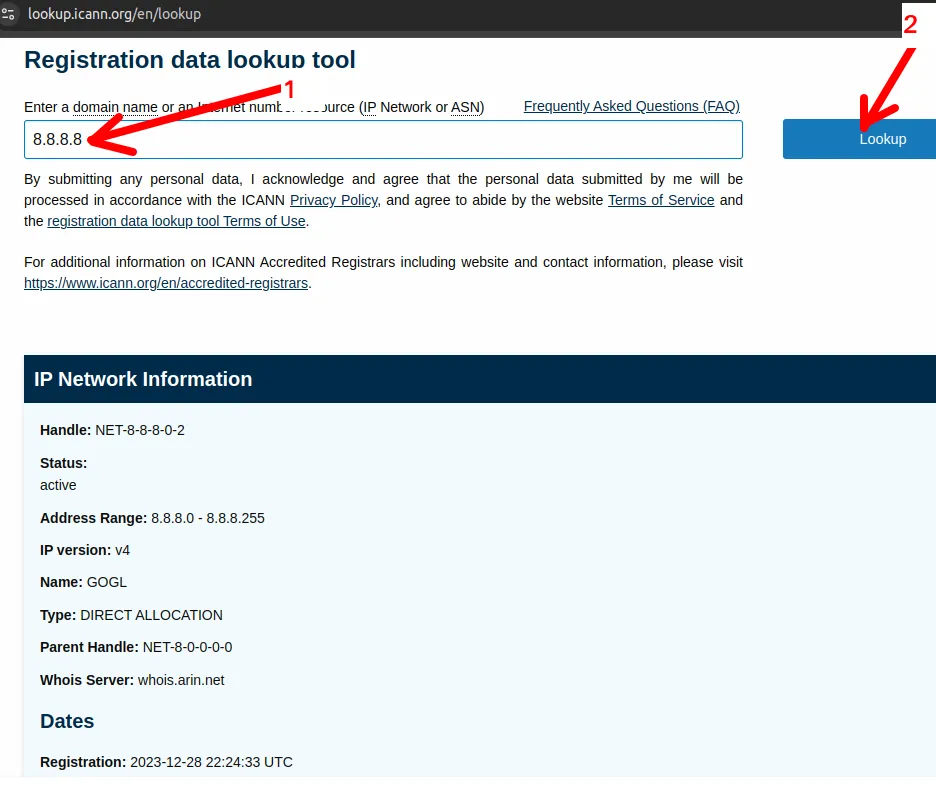
Besides checking websites, ICANN’s RDAP tool also allows obtaining information about IPs. In this case, we will enter an IP and then click “Lookup”.
We can see in the figure below that we have information about the IP registration.
Relevant Information in a WHOIS / RDAP Query
Below are some important pieces of information we can find in a WHOIS / RDAP query.
Domain Name: Refers to the full name of the domain registered on the Internet, such as “simplificandoredes.com,” which is unique and identifies a site or service.
Domain Registration: Provides the name of the registrar managing the domain, i.e., the company or organization responsible for the domain’s administration and renewal.
Creation and Expiration Dates: The date the domain was first registered (creation) and the date the current registration will expire, meaning when the owner will need to renew the domain to keep it active.
Owner Name and Address: Contains the domain owner’s details, including the full name or organization and the physical address associated with the registration.
Contact Information: Refers to the domain owner’s or administrator’s contact details, such as phone numbers and email, to enable communication if needed.
Name Servers (DNS): Indicates the name servers configured for the domain, which are responsible for translating the domain name into an IP address, allowing the location and access to the associated site or service.
Did you enjoy learning more about WHOIS and RDAP? Browse more on the site, and you will find several other important topics for your learning.
See more:
HTTP Protocol – How Does It Work?

Juliana Mascarenhas
Data Scientist and Master in Computer Modeling by LNCC.
Computer Engineer

